Vulval and vaginal problems
Vaginal discharge and lower genital tract infections
Most of the time, vaginal discharge is normal (depending the time in your menstrual cycle). However, if the color, smell, or consistency seems significantly unusual, especially if it accompanied by vaginal itching or burning, you could have an infection or other condition, e.g. tumors, polyps, etc. Your doctor will perform a physical examination and maybe some investigations (e.g. take swabs from the discharge for culture, cervical smear) to establish the diagnosis and hence proper treatment.
Some tips for preventing vaginal infections that can lead to abnormal discharge:
- Keep the vagina clean by washing regularly with a gentle, mild soap and warm water.
- Never use scented soaps and feminine products or douche. Also avoid feminine sprays and bubble baths.
- After going to the bathroom, always wipe from front to back to prevent bacteria from getting into the vagina and causing an infection.
- Wear 100% cotton underpants, and avoid overly tight clothing.
Bartholin’s cyst
The Bartholin’s glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. These glands secrete fluid that helps lubricate the vagina. Sometimes the openings of these glands become obstructed, which result in a swelling called a Bartholin’s cyst. If the fluid within the cyst becomes infected, you may develop a collection of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue (abscess).
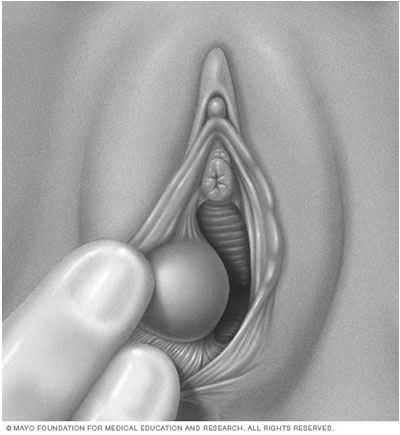
Marsupialization (a minor operation where the inner cyst wall is folded back and stitched to the skin) is the treatment of choice. Antibiotics will be prescribed if it is infected.



